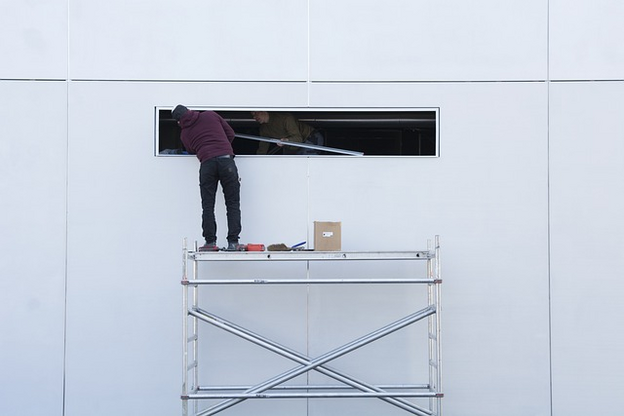
Scaffolding mishaps abound in the construction industry. You’ll often hear of falls from heights or scaffolding collapsing, leading to deaths and injuries. Falls, slips, and trips from a higher to a lower level were responsible for over 33% of construction deaths in 2021. This calls for extra safety precautions when installing and using these support structures.
The risks can be considerably minimised if you follow recommended safety guidelines. That’s the focus of this article, particularly exploring critical safety practices for interior scaffolding. Read on to ensure your workspace is safe for everyone.
- Pre-work preparations
It’s critical to undergo adequate training before working on a scaffold. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides guidelines on how to train workers to erect, use, and disassemble scaffolding. Knowing these essentials helps prevent accidents.
Choose scaffolding that matches your project’s demands. An important consideration here is the weight capacity. The scaffold must support the loading, including the workers and construction materials. The joining of the members should also be intricate to avoid a wobbly platform with a high likelihood of tipping over or warping underweight.
Carefully inspect the scaffolding components to identify defects. Don’t use any members with faulty or missing parts, as such weak points could cause the entire erection to come tumbling down. A reliable interior scaffolding rental company should provide you with scaffolding that’s in excellent condition. Meanwhile, note that an abundance of defective parts indicates untrustworthiness.
Finally, prepare your site before assembling the scaffold. Get the necessary permits from the local authority. Consider dangers like electrical lines and uneven surfaces and see how to work around them.
- Safe erection and disassembly
Follow the scaffold manufacturer’s instructions in the letter. About 50% of people never read the user manual for devices and equipment, which often leads to hitches. Different scaffold types have varying assembling procedures and nuances. Ignoring these guidelines sets you up for accidents.
Ensure the base is firm. Don’t place the base plates on unstable ground. You can add ballast around them for more stability. Moreover, level the scaffold bases as much as possible to make the structure upright.
Connect all components correctly, from pins to braces and wedges. They’re all meant to make the assembly rigid for proper support. Leaving out some members may make the structure wobbly, increasing the chances of accidents.
It also helps add guardrails and toeboards to act as barriers, safeguarding workers from fatal falls if they trip or slip up there.
- Working on the scaffold
Install safe access points and movement areas on the scaffold. Ladders help a lot in climbing to higher points. They’re safer than using the scaffold itself to ascend in a monkey-like fashion.
Personal fall arrest systems, including harnesses and lanyards, are also critical. The construction industry is especially notorious for falls. In 2021, 46.2% of all fatal falls, slips, and trips were from this sector. Thus, you must be strict with fall prevention.
Require workers to wear such fittings whenever working up scaffolds. Attach them securely onto immovable anchors capable of supporting the weight of a falling person. These could be a building beam or a unique anchor system installed for fall protection. The anchor point should be separate from the scaffold itself.
Keep your work area clean and free of unnecessary items. Objects placed haphazardly around the construction site can lead to trips. Use approved hosting strategies for materials to maintain balance and prevent the scaffolding from tipping over due to imbalance.
As work progresses, watch out for the weather, too. Strong winds can penetrate the interiors and destabilise the scaffold. Staying vigilant can help mitigate hazards.
- Communication and teamwork
Clear communication among workers allows the team to identify potential hazards and brainstorm safety precautions. Encourage them to be open and voice their concerns regarding any impending threat.
Appoint a site supervisor to monitor activities, enforce safety rules, and address workers’ concerns. They’re the point of contact between the workers and the management.
But beyond the supervisor, encourage all workers to be watchful always. Urge them to actively look out for each other and notify the management about any threat to safety. After all, the overseer’s eyes can’t be everywhere. A collaborative approach makes the work environment considerably safe.
- Emergency procedures
Draft an emergency plan outlining evacuation procedures, first aid conventions, and emergency contacts. Establishing a straightforward response plan lets workers know how to react when disaster strikes.
It helps install extinguishers at strategic spots across the construction site for fires. Also, workers should familiarise themselves with evacuation routes.
And for medical emergencies, first aid comes in handy. Also, have contact information for emergency health services should there be a need to call them to save a life. Prompt response can genuinely save lives.
Conclusion
Scaffolding is essential during interior renovation and repair works. But it carries several risks since it involves working at heights. The safety protocols highlighted herein will help mitigate accidents during your construction project.
Professional training in scaffold safety is also necessary. Such lessons deepen your team’s safety awareness. You’d also want to conduct regular safety audits and emergency drills to better prepare your team for the worst.
Ultimately, safety on scaffolding ensures your project progresses to completion without loss of lives, injuries, and property damage.




 POSTED BY
POSTED BY