Energy efficiency has steadily emerged as a keystone in conserving our planet’s finite resources. It is also a key determiner of how we manage our household budgets. Given the rise in energy costs and the awareness of the finite nature of natural resources, the importance of home energy efficiency has never been greater. One strategy for homeowners to understand their home’s energy use and potentially lessen it is conducting a DIY home energy audit. Common energy drains are waiting to be identified and attended to within Australian homes and homes worldwide. This guide seeks to understand these energy zappers with the intent to reduce energy costs and environmental impact.
Understanding Your Home’s Energy Use
Every home has a unique rhythm, with different routines, family sizes, lifestyle preferences, and schedule variations. All these elements contribute to how energy is utilised, leading to distinct consumption patterns. Certain appliances and systems within our homes stand out for their higher energy use. HVAC systems (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), water heaters, refrigerators, washing machines, dishwashers, entertainment systems, and lighting, for instance, consume more energy than others.
Monitoring your energy bills over time provides information about your typical electricity bill factors. For instance, high energy use in winter might be due to the excessive use of electric heaters, or the trend of hot water usage could indicate an inefficient water heating system. Monitoring gives you the quantitative information required to manage your energy use better and make necessary adjustments.
Technological advancements have given us tools and apps to help in this regard. These allow you to monitor energy consumption in real-time, set energy-saving preferences, and even receive alerts and reports about unusual energy consumption patterns.
How to Conduct a DIY Home Energy Audit
A DIY Home Energy Audit is like a physical examination of your home. You systematically investigate the various elements that might contribute to energy inefficiency.
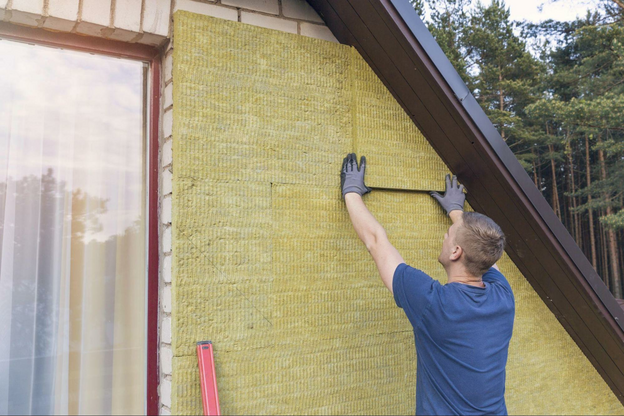
1. Inspecting Insulation and Sealing Leaks: Much of a home’s heating or cooling energy can be lost due to poor insulation and cracks that allow air leakage. Begin your audit by checking the insulation in your home, particularly in the attic and walls. Compare your insulation level to the guidelines provided for homes in your area. Insulation thickness will depend on the material used, so it’s not just about the depth of the insulation. During inspection, you typically also check for moisture, which could compromise the effectiveness of your insulation.
Sealing leaks is another energy-saving measure you can institute. Check for drafts around windows, doors, vents, recessed lights, plumbing fixtures, and electric outlets. Small gaps and cracks may seem insignificant, but they add up, resulting in unnecessary energy loss. For instance, caulking and weatherstripping windows and doors can significantly improve your home’s energy efficiency by preventing drafts.
2. Evaluating Heating and Cooling Systems: Among the biggest energy consumers in a house are the HVAC units. Regular maintenance of these systems is crucial to ensure they function efficiently. Your home heating and cooling evaluation should include cleaning or replacing air filters, inspecting furnace ducts for leaks, obstructions and dust buildup, examining your fireplace for leaks or airflow issues, and checking that the radiator and water heaters are adequately insulated.
3. Checking Windows and Doors for Drafts: Ineffective window and door sealing can also contribute to potential energy leakage. Issues like damaged seals or gaps can let outside air seep in, forcing your heating and cooling system to work harder. Therefore, check all exterior doors and windows for drafts and consider installing weatherstripping or door sweeps where necessary. Using caulking or foam seals to seal gaps around window and door frames can help maintain a constant indoor temperature, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
Identifying and Fixing Common Energy Drains
Energy drains within a home are often unsuspecting appliances or practices that sap energy quietly and insidiously. Here’s how you can tackle them:
1. Lighting: Energy consumed by lighting can account for around 10-15% of your power bill. The simplest way to save energy here is to replace incandescent bulbs with more efficient alternatives like LED or CFL bulbs. While these are slightly more expensive initially, they offer significant energy savings over their lifespan. Another tip is to use task lighting, illuminating only the areas where you’re working instead of lighting up an entire room.
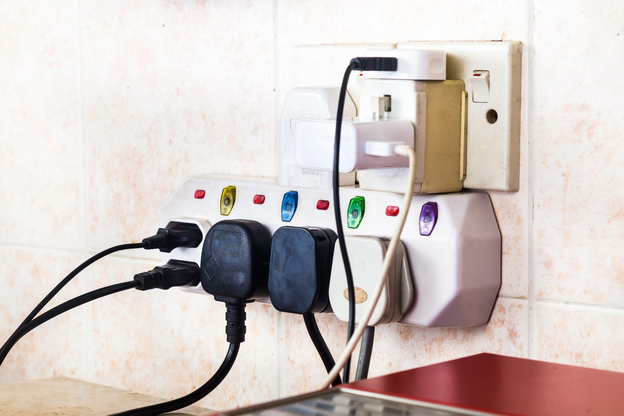
2. Appliances: Large appliances like washing machines, dryers, and fridges are notorious energy drains. Switching to appliances with better energy efficiency ratings can help reduce their energy-draining effects. Even smaller appliances and gadgets can continue to use power in their standby mode, a phenomenon termed ‘phantom load’. Unplugging these gadgets or using a power strip with switches can help you control this energy leakage.
3. HVAC Systems: Your HVAC system can cost substantially if not tended to. Regular maintenance checks, cleaning or replacing filters and ensuring ducts are correctly sealed can all contribute towards running your HVAC system optimally.
4. Water Heaters: Traditional water heaters constantly heat large volumes of water, which can use significant amounts of energy. More efficient alternatives, like tankless or on-demand water heaters, heat water only when needed, resulting in considerable energy savings.
Cost-Effective Energy-Saving Solutions
Here, we’ll look at some cost-effective solutions to address energy inefficiency within your home. Solutions that are friendly on your pocket as well as on the environment.
1. Insulation Improvements: Improving insulation in your home is a cost-effective way of reducing energy consumption by maintaining optimal indoor temperatures. Even simple actions such as sealing holes, gaps or cracks can make a difference by preventing outdoor air from infiltrating your home. For more significant improvements, consider upgrading to high-quality insulation materials.
2. Smart Thermostats: A smart thermostat can optimise your energy usage by learning your preferred temperature settings and routine and then adjusting your heating and cooling accordingly. These clever devices can sense when you’ve left your home and adjust to an energy-saving setting. Some models even allow you to control them remotely via a mobile app.
3. Window Treatments: It might surprise you, but your choice of window treatments can significantly affect your energy efficiency. Curtains, shades or blinds can offer additional insulation, reducing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. Look for thermal curtains or honeycomb blinds explicitly designed to enhance insulation.
4. Weather-Stripping and Caulking: Sealing gaps around windows and doors with weather-stripping or caulking is a potent and economical way of conserving energy. These materials last several years and can be easily installed with simple tools.

Long-Term Strategies for Energy Efficiency
While immediate fixes are essential, a long-term plan is critical to sustainable energy conservation.
1. Investing in Renewable Energy Sources: Although the upfront cost might seem high, investing in renewable energy sources like solar panels can provide substantial long-term savings. Moreover, depending on your location, this shift could help you become power-independent and sell excess power back to the grid.
2. Home Energy Management Systems: A home energy management system monitors and controls energy usage at the macro level, including lighting, heating, cooling, security, and more. This intelligent technology enables customers to reduce energy consumption, providing real-time data, thus making it easier to manage power use.
3. Regular Maintenance Schedules: Regular maintenance of your HVAC, water heating, and electrical systems helps optimise their performance, resulting in significant energy savings. Semi-annual or annual servicing is recommended for most systems.
4. Educating Household Members: Finally, change starts with education. Informing your household members about the importance of energy conservation and sharing tips and tricks for achieving it is crucial to ensure all your efforts are worthwhile.
Conclusion
A DIY home energy audit is a practical way to understand where your energy goes and how it might be better managed. Identifying and addressing common energy drains eliminates wasteful consumption, leading to lowered energy bills and lesser environmental impact. Regular assessment and maintenance, coupled with adopting cost-effective and long-term energy-saving measures, builds an environment of mindfulness regarding energy usage. After all, every effort to reduce energy consumption, big or small, is a step towards a healthier planet.




 POSTED BY
POSTED BY